Deploying a server can be a transformative decision for a small business, providing opportunities for enhanced security, reliability, centralized data management, and future growth. Whether you are upgrading from a basic peer-to-peer network or implementing your first centralized IT system, having a physical server can streamline workflow, reduce risk, and ensure compliance with data security standards. Physical servers also provide a tangible, on-site presence for IT resources, making management, monitoring, and troubleshooting much more accessible to in-house staff. By following carefully established practices, businesses can avoid common pitfalls and optimize their server investments. Solutions such as tower server solutions from Nfina are particularly suitable for business owners seeking both flexibility and scalability to fit their unique needs, as they often include options for expansion and customization suited to small business applications. By using these solutions, organizations can achieve the security and reliability typically reserved for enterprises, while still offering packages manageable for smaller IT teams.
Before integrating a server into daily operations, business owners must weigh not only hardware specifications but also environmental factors, physical setup, and maintenance strategies. Ignoring these considerations could lead to unforeseen challenges that affect both productivity and data integrity. Failure to consider even one of these elements can result in underperformance, avoidable downtime, or security gaps. Each piece of the deployment puzzle plays a critical role in supporting data integrity and minimizing downtime, ultimately ensuring that the server supports business operations effectively and grows alongside the company’s ambitions. Proper planning at the outset sets the stage for effective resource use and reliable support as you scale. Taking the time to thoroughly evaluate these aspects up front will pay dividends in reduced stress and smoother daily operations down the road.
Choosing the Right Tower Server
The foundation of a reliable IT infrastructure begins with selecting the appropriate tower server. Consider crucial specifications such as processing speed, memory capacity, and storage configurations. Processing power impacts not only day-to-day performance but also determines whether the server can handle specialized business applications or large file transfers without lag. Memory capacity allows multiple users to access files and applications simultaneously, avoiding slowdowns during peak usage. Adequate, upgradable storage ensures the server can accommodate growing volumes of business data, important documents, and system backups as your business evolves.
When assessing choices, pay attention to options that easily scale to meet emerging requirements, such as increased storage or network expansion. Look for models that can accommodate additional drives or network cards as the company grows, as well as support for virtualization if you plan to run multiple server roles. Support for advanced virtualization also enables the consolidation of multiple IT functions onto a single physical device, reducing hardware costs while maintaining flexibility. The ability to tailor hardware reduces the need for future overhauls and maximizes return on investment by enabling gradual upgrades rather than complete replacements.
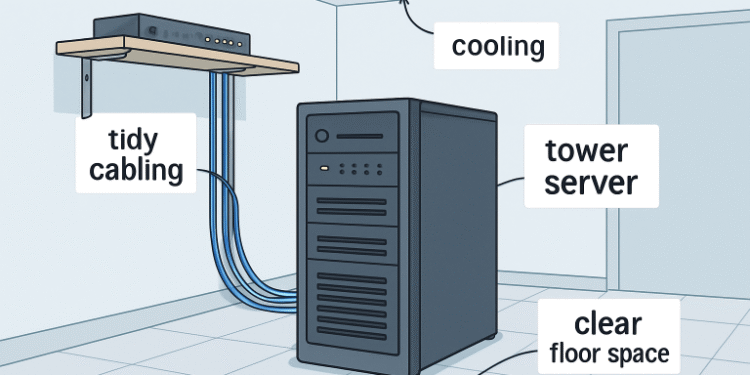
Optimizing the Server Room Environment
A dedicated, well-maintained environment is indispensable for server longevity. Key environmental factors include temperature, ventilation, and cleanliness, each of which plays a vital role in ensuring the electronics operate reliably for years to come. Servers generate significant heat when operating at full capacity, and even a few degrees above the optimal range can accelerate component decay or trigger emergency shutdowns. An unregulated environment can cause overheating, increased dust accumulation, or even moisture-related failures, all of which can cut the life of expensive hardware short and decrease the reliability of your IT operations.
- Temperature Control: Maintain a stable temperature, ideally between 68°F and 72°F, as fluctuations can cause heat-related hardware failures. Overheated servers are more prone to random shutdowns and permanent damage to sensitive components.
- Ventilation: Ensure air circulation around the server to efficiently disperse heat. In cramped areas, install supplementary fans or vents to prevent overheating. If possible, designate an area of the office exclusively for IT equipment to help manage airflow.
- Cleanliness: Dust and debris reduce airflow and can cause component damage, making regular cleaning a necessary task. Vacuum the area regularly and keep food and drink away from electronic equipment. This practice also reduces the risk of attracting pests or humidity, both of which can damage electronics.
Implementing these conditions helps prevent premature hardware issues and maintains optimal operational efficiency, making it easier to monitor temperature and airflow, and preventing the gradual buildup of dust that could cause failures over time. Businesses with limited office space should consider enclosures or dedicated cabinets with integrated cooling solutions to manage these factors within a smaller footprint.
Implementing Effective Cable Management
Effective cable management not only contributes to a tidy appearance but also enhances safety and troubleshooting ease. In small business settings where multiple devices are connected to the server, tangled or unlabeled cables can quickly become a hazard, making it difficult to identify issues or add new equipment without risking downtime. Neat cabling practices also reduce the risk of accidental unplugging or cable damage during cleaning or equipment rearrangement, which can disrupt operations.
- Labeling Cables: Mark each cable for quick identification and efficient problem resolution. This minimizes the risk of disconnecting the wrong device during troubleshooting or maintenance.
- Using Cable Trays: Organize wiring neatly with trays or channels to avoid tangles and accidental unplugging. This keeps pathways clear and ensures cables remain off the floor, preventing trip hazards and dust accumulation.
- Regular Audits: Reevaluate the cabling setup periodically to ensure the organization remains intact and to accommodate new connections. Removing obsolete cables also reduces clutter and improves airflow around hardware.
Reliable cable management saves time during routine maintenance and prevents service interruptions caused by disconnections or congestion. Meticulous organization also increases the efficiency of hardware upgrades or expansions, and ensures that potential hazards, such as electrical shorts from damaged cords, are minimized. This becomes even more important if you ever expand to multiple servers or need to swap hardware quickly.
Ensuring Uninterruptible Power Supply
Protecting your hardware investment from sudden power interruptions is paramount. Power failures can result in lost data, corrupted files, or even physical damage. Incorporating an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS), such as the APC Smart-UPSline, shields your infrastructure from blackouts, voltage drops, and other electrical anomalies. A robust UPS setup provides automatic failover, maintaining power long enough for a safe, controlled shutdown or a transition to backup energy sources.
For businesses in regions prone to outages or electrical instability, this is an indispensable safeguard. Electrical surges and brownouts are common causes of server component failure, yet they can be easily prevented by deploying a UPS system. A UPS also provides the critical minutes needed to perform safe shutdowns or manage workloads during extended outages. Evaluate the capacity and runtime offered by various UPS systems to ensure that vital operations, such as data backup processes, can be completed securely.
Prioritizing Security Measures
The importance of a multi-layered security posture cannot be overstated. Secure your physical workspace by limiting server room access to trusted staff only and considering locks or badges for additional protection. On the digital front, implement firewalls and real-time intrusion detection systems to defend against unauthorized attempts and vulnerabilities such as malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks.
Setting up user permissions and network access controls further limits the risk of internal breaches. Implementing network segmentation, where possible, adds another layer of protection by restricting communication between critical systems and regular user workstations. Keeping system software, firmware, and antivirus databases up to date is integral to fortifying defenses and protecting sensitive data from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. Security audits, both internal and external, can help reveal gaps in your protections that automated tools might miss, ensuring long-term security compliance.
Planning for Scalability
As operations expand, so will the demands placed upon your server infrastructure. Choose servers built with scalability in mind, with room for extra drives, memory slots, and additional CPUs.
The right choice now makes adding new roles, such as email hosting or cloud backup support, straightforward as your needs change. Plan your initial purchases so that workload-balancing or role expansion can be done with minimal disruption. Prioritizing upgradable solutions now avoids costly, disruptive hardware replacements down the line, helping ensure your business does not outgrow its technology. Small businesses should always keep an eye on future needs, so that expansion can be managed proactively and affordably, rather than reactively.
Establishing Regular Maintenance Protocols
Scheduled maintenance enhances both uptime and server health. Allocate regular intervals to perform the following maintenance tasks while documenting every step taken:
- Software Updates: Update the operating system, applications, and firmware to mitigate vulnerabilities and improve performance. Out-of-date systems are targets for cyber threats, and frequent updates are an easy way to stay protected.
- Hardware Checks: Visually inspect hardware for damage or wear, and replace any failing components before they cause outages. Look for signs such as unexpected noises, overheating, or inconsistent system behavior.
- Data Backups: Plan automated, frequent data backups to external drives or cloud storage, ensuring swift recovery in the event of unforeseen failures. Test backup integrity periodically to guarantee data can be restored if needed.
By adhering to a proactive maintenance plan, organizations maximize system reliability and extend the effective lifespan of their IT assets. Automating update checks and using scheduled maintenance reminders helps ensure nothing is overlooked, even as your business scales. Keeping accurate maintenance records identifies recurring issues and ensures warranty claims are processed effectively, if necessary.
Final Thoughts
Deploying a tower server can unlock greater productivity, stability, and growth potential for any small business. By thoughtfully selecting hardware, optimizing the physical environment, maintaining organized cabling, guaranteeing steady power, implementing robust security, planning for expansion, and adhering to ongoing maintenance routines, business owners ensure their IT backbone stands ready to support future goals. When all these best practices are approached strategically, even a modest technology investment can offer years of reliable, responsive service for a fast-growing business. Embracing a culture of proactive IT care not only conserves resources but also positions your business for future digital transformation.